Welcome to my quick guide how to install self-hosted Akaunting web application. Akaunting is a very good open source accounting software. It is 100% free to use and customize because it is open source. It is built solidly using PHP and Laravel and stores data using MySQL server.
Here is the link to Akaunting project official website:
https://www.akaunting.com
Before you get started you may want to install LEMP (linux nginx mysql and PHP) first.
I have a quick 10 minute guide here:
https://ubuntu-server-how-to-tips-tricks.blogspot.com/2019/10/installing-lemp-linux-nginx-mysql-php.html
in this example I am going to store my akaunting software in /data_local/app/www/akaunting
yours may be different such as /var/www/akaunting
After you have LEMP installed you can start installing Akaunting:
DOWNLOAD AND COPY AKAUNTING ZIP FILE FROM THIS URL
https://akaunting.com/thank-you
PREPARE THE DESTINATION DIRECTORY
mkdir -p /data_local/app/www/akaunting
UNZIP THE AKAUNTING ZIP FILE (adjust filename as necessary for different version)
unzip Akaunting_1.3.17-Stable.zip
SET CORRECT PERMISSION ON DESTINATION DIRECTORY
chmod -R 775 /data_local/app/www/akaunting
chown -R www-data:www-data /data_local/app/www/akaunting
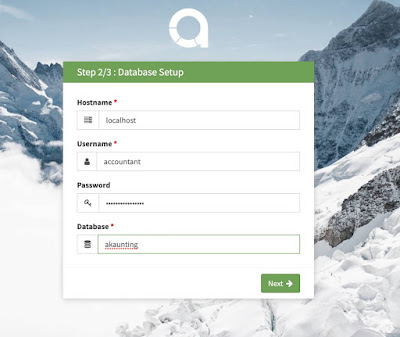
SETUP MYSQL DATABASE, USER AND PERMISSIONS
sudo mysql
create database akaunting;
create user accountant@localhost identified by '<your_password_here>';
grant all privileges on akaunting.* to accountant@localhost;
flush privileges;
exit;
INSTALL ADDITIONAL PHP MODULES AS REQUIRED BY AKAUNTING
sudo apt install php-imagick php7.2-gd php7.2-curl php7.2-zip php7.2-xml php7.2-mbstring php7.2-bz2 php7.2-intl
SETUP NGINX CONFIGURATION FILE USING THE FOLLOWING TEXT
nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
server {
listen 80 default_server;
# listen 443 ssl http2;
# ssl_certificate /ssl/crt/file.crt;
# ssl_certificate_key /ssl/key/file.key;
server_name _;
root /data_local/app/www/akaunting/;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
index index.html index.htm index.php;
charset utf-8;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
# Prevent Direct Access To Protected Files
location ~ \.(env|log) {
deny all;
}
# Prevent Direct Access To Protected Folders
location ~ ^/(^app$|bootstrap|config|database|resources|routes|storage|tests|artisan) {
deny all;
}
# Prevent Direct Access To modules/vendor Folders Except Assets
location ~ ^/(modules|vendor)\/(.*)\.((?!ico|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|js|css|less|sass|font|woff|woff2|eot|ttf|svg).)*$ {
deny all;
}
error_page 404 /index.php;
# Pass PHP Scripts To FastCGI Server
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock; # Depends On The PHP Version
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /\.(?!well-known).* {
deny all;
}
}
sudo systemctl nginx reload
GO TO BROWSER AND FINISH CONFIGURATION
Just follow the rest of the guide / wizard from the Akaunting.
Congratulations! You have just installed a free and powerful accounting software for your business!
REVERSE PROXY SETTING
If you are using Akaunting behind reverse proxy, make sure you add this setting:
fastcgi_param HTTPS 1;
This setting saved my day!